¶ Virtual Power Plant
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) is a technology that combines various distributed energy sources, such as solar panels and batteries, to create a virtual power plant array.
The hybrid inverter is a device that functions both as a solar inverter and a battery inverter in a single unit. Typically installed in private homes, it utilizes solar panels to produce electricity and stores excess energy in a battery that can be used later when the sun is not shining.
The VPP in connection with the hybrid inverter enables control of energy production and consumption in your home. If there is excess energy, the VPP can send it back to the grid, and if more energy is needed, it can draw energy from the batteries.
By optimizing energy consumption, the VPP in conjunction with the hybrid inverter can contribute to reducing the costs of energy consumption and at the same time stabilize the overall energy grid. This makes it possible to utilize renewable energy sources more efficiently and sustainably.
¶ Mode
Through CleverHouse you can manage your VPP management. Below is a description of all the modes and functionalities we support.
¶ Paused
This setting allows you to temporarily cut off communication with the inverter so that you can control it manually through its own display without interfering with our algorithms.
¶ Off
When this setting is enabled, the inverter will neither charge nor discharge the battery. The inverter will continue to produce AC power from your solar panels.
¶ Charge fully
This setting forces the inverter to charge at full power until the battery has reached 100% or you have changed the setting.
¶ Discharge fully
This setting forces the inverter to discharge at full power until the battery has reached the lowest legal SOC (State of charge) or when the setting is changed.
¶ Automatic
This option opens a new dropdown list of our Virtual Power Plant (VPP) algorithms. These algorithms can be used on your hybrid inverter to automatically and intelligently manage the charging and discharging of your battery using excess solar energy or even based on current electricity prices.
¶ Algorithm
¶ SimpleFlow
In Simple mode, the VPP acts as a standard hybrid inverter controller, controlling the operation of the inverter. The aim is to achieve a zero measurement on the house's electricity meter as far as possible. If the home's power consumption is positive, the inverter will start supplying the home with power from the battery. If there is negative consumption, the inverter will start charging the battery to avoid sending excess current back to the grid. This is done to optimize the use of solar energy and minimize the costs of electricity consumption in the home.
¶ State
VPP has 7 different modes:
- Paused (The system has no control over the inverter. In this state, the inverter can be controlled by another service):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Forced discharging (Discharges the battery to the mains):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Discharging allowed (The battery tries to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Charging allowed (The system allows charging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Forced charging (Charges the battery from the mains):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Self consumption (The system allows both charging and discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm is only in this state.
- Off (The system works like a regular grid-connected inverter, where solar production is sent to the grid without charging or discharging the battery):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
¶ UserFlow
UserFlow is more intelligent, where you have the option to configure it according to your wishes. Here you can help determine the limits for when the battery must be discharged from the mains (e.g. at a cheap mains price), and at what price level you would like to discharge your battery.
By clicking on "Setting the electricity price" you get 4 parameters that you must adjust according to your wishes. If in doubt, leave them at their default values.
- Max charging percentage your battery may charge from powernetwork: This parameter works together with "Max buy price" and helps determine how much the battery can be charged when the power price is within the range determined by "Max buy price". You can adjust this parameter from 0 to 100% 100% means you want to fully charge the battery.
- Charge the battery from the power grid when the hourly price is less than: This setting determines when the electricity price is low enough to charge the battery directly from the mains. This parameter can be set from 0 to 200%. 100% means that if the average price for the day is DKK 5/kWh, the system will start charging the battery when the hourly price is DKK 5 or less. If, on the other hand, you choose 50%, the battery will only start charging when the hourly price reaches DKK 2.50 or less.
- Do not charge when the hourly price is greater than (upper limit): This parameter ensures that the energy in the battery is used when the electricity price is high. If the average price for the day, e.g. is DKK 2.5, then a setting of 200% will mean that the system will always try to take the energy from the battery if the electricity price within the hour is higher than DKK 5. This limit also limits the inverter from charging the battery with excess current, as it gives more value to sell to the electricity grid during the expensive periods. The parameter can be set between 0 and 200%
- Do not discharge when the hourly price is less than (lower limit): This parameter ensures that the energy in the battery is preserved when the electricity price is too low. If the average price for the day, e.g. is DKK 5, then a setting of 50% will mean that no energy is taken from the battery if the electricity price is below DKK 2.5. The parameter can be set between 0 and 200%.
The graph above shows a visualization of the limit values that have been set.
The upper limit: During the day, if the electricity price exceeds the specified limit value (marked in red). The system will then supply the house with energy from the battery as the electricity price is high. This algorithm does not take into account future consumption and
The lower limit: During the day, if the electricity price is lower than the specified limit value (marked in green). Then the system will take energy from the grid as the electricity price is low and the battery's energy is stored for when the electricity price is high.
Between upper and lower limit values, the system runs the Simple algorithm, as described above.
The difference between upper limit and auto is that if on a given day the house has 1 kwh in consumption and solar cells produce 4 kwh. Will the system in auto, cover the 1 kwh consumption from the solar cells, and put the remaining 3 kwh in the battery. If, on the other hand, the system is in the upper limit, in the same example, the 1 kwh consumption from solar cells would be covered, and the remaining 3 kwh would then be sold to the electricity grid.
¶ State
VPP has 7 different modes:
- Paused (The system has no control over the inverter. In this state, the inverter can be controlled by another service):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Discharge completely (Discharges the battery to the mains):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Zero export (The system allows discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- If the electricity price is above the upper limit.
- Zero import (The system allows charging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- If the electricity price is below the lower limit.
- Charge fully (Charges the battery from the mains):
- If the electricity price is below Max charging and Max purchase price.
- Self consumption (The system allows both charging and discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- If the electricity price is between the upper limit and the lower limit, and current is sold to the electricity grid (negative effect on the main meter) or there is current consumption in the house (Positive effect on the main meter)
- Off ( The system works like a regular grid-connected inverter, where solar production is sent to the grid without charging or discharging the battery):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
¶ SmartFlow Consumption
At its core, SmartFlow is a sophisticated algorithm designed to find as many charge/discharge cycles as possible throughout the day. This means that the algorithm constantly monitors the electricity prices, the energy consumption in your home, and the expected solar production on DC-coupled systems (Expected solar production from AC-coupled systems is not currently implemented). It adjusts the power flow accordingly to ensure you always get the best possible price for your energy.
The SmartFlow algorithm is designed to work seamlessly with your Kstar hybrid inverter and is fully automated. Then you don't have to worry about manually managing the energy in your home with cumbersome settings.
The SmartFlow algorithm controls the charging and discharging of the battery based on several factors. It takes into account the historical electricity consumption in the house, the expected production from the solar cells, and electricity prices. All on an hourly basis.
Using this information, SmartFlow generates a comprehensive plan that determines the optimal time to charge the battery. It utilizes historical electricity consumption patterns to identify periods of high electricity consumption and expensive electricity prices. During these periods, when electricity costs are typically higher, SmartFlow uses the stored energy in the battery instead of depending on the electricity grid.
¶ State
VPP has 7 different modes:
- Paused (The system has no control over the inverter. In this state, the inverter can be controlled by another service):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Discharge completely (Discharges the battery to the mains):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Zero export (The system allows discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Zero import (The system allows charging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- If it is determined that the battery should be used for discharging at a later point and if it is allowed to charge due to the price of electricity, it will go into this state.
- Charge fully (Charges the battery from the mains):
- If it is determined that the battery shall charge it will go into this state
- Self consumption (The system allows both charging and discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- If the system has determined this is a expensive hour, it will go into this state
- Off (The system works like a regular grid-connected inverter, where solar production is sent to the grid without charging or discharging the battery):
- If it is determined that the battery should be used for discharging at a later point and if it is not allowed to charge due to the price of electricity, it will go into this state.
If a more detailed desacribtion is needed please read this: LINK
¶ SmartFlow Buy/Sell
SmartFlow Buy/Sell is a version of SmartFlow Consumption. This algorithm ignores your historical and current consumption and the power meter. The algorithm determines the most economical charging and discharging of the battery by only looking at the hourly price of electricity. Thus charging the battery from the grid at low prices and discharging at high prices.
The algorithm will still find the highest possible number of charge/discharge cycles in order to maximize the revenue.
¶ States
VPP has 7 different modes:
- Paused (The system has no control over the inverter. In this state, the inverter can be controlled by another service):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state.
- Discharge completely (Discharges the battery to the mains):
- If it is determined that the battery shall discharge it will go into this state.
- Zero export (The system allows discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state
- Zero import (The system allows charging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state
- Charge fully (Charges the battery from the mains):
- If it is determined that the battery shall charge it will go into this state
- Self consumption (The system allows both charging and discharging the battery to get the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot get the system into this state
- Off (The system works like a regular grid-connected inverter, where solar production is sent to the grid without charging or discharging the battery):
- If it is determined that the battery should be used for discharging at a later point and if it is not allowed to charge due to the price of electricity, it will go into this state.
¶ Peak-Shaving
Peak-shaving is a method to reduce the load on the power grid by using stored energy from a local battery. This is done by discharging the battery via a hybrid inverter during periods of high electricity demand.
Imagine you have a fuse that allows a maximum current consumption of 100 amps. You plan to use a large electrical device that requires an additional 50 amps, which would exceed the fuse's capacity and potentially cause an overload.
In this case, our algorithm will detect the increased power demand. It will automatically start discharging the battery to supply the extra 50 amps. This way, you can continue using your electrical device without overloading the fuse or the power grid.
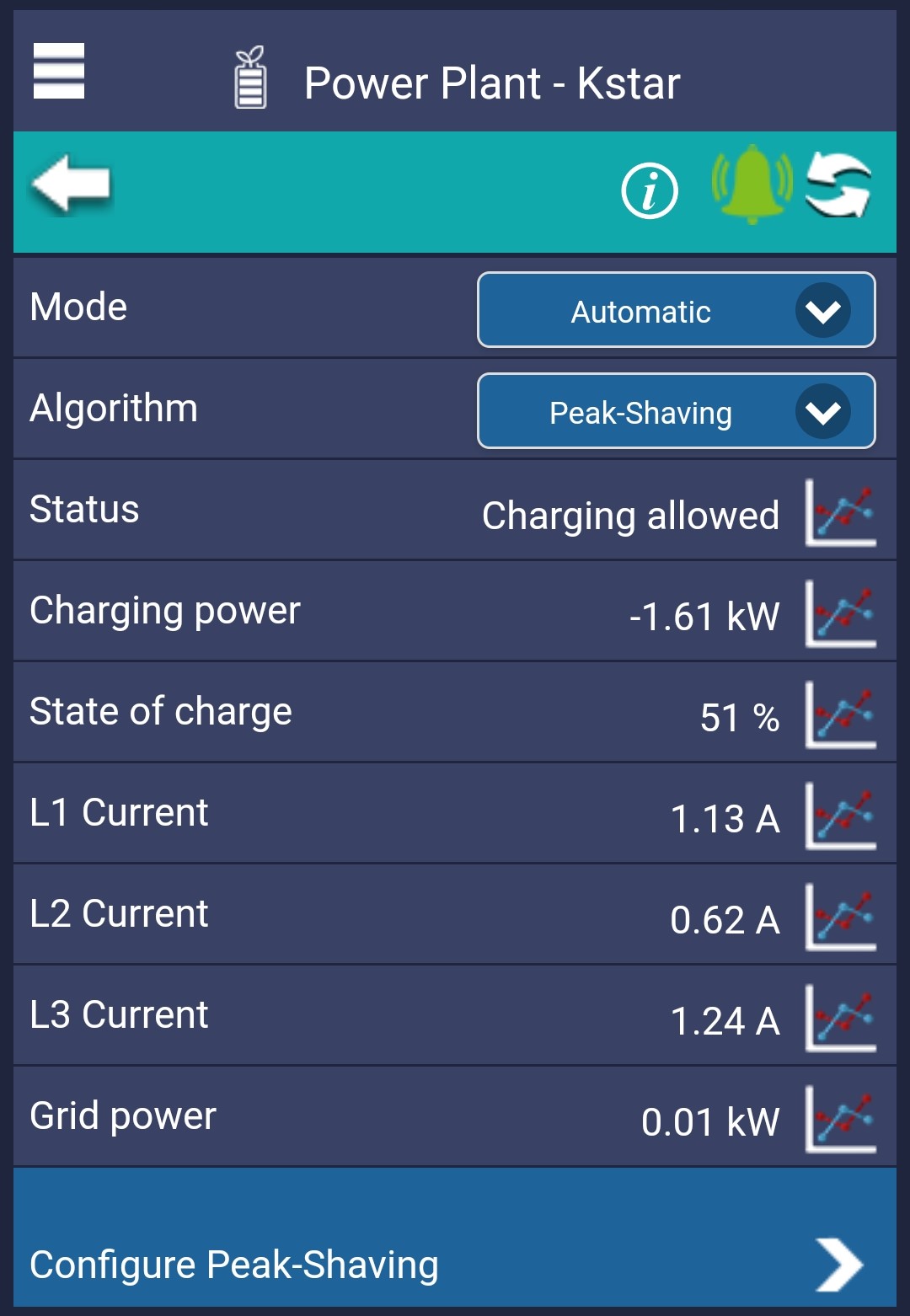
To set up peak-shaving, an import limit must first be added to the installation. This limit cannot be configured by the customer. The import limit is used to calculate when the battery should start discharging if one of your phases approaches the limit.
Next, you can click on Configure Peak-Shaving, where you will have the option to further set up your Peak-Shaving
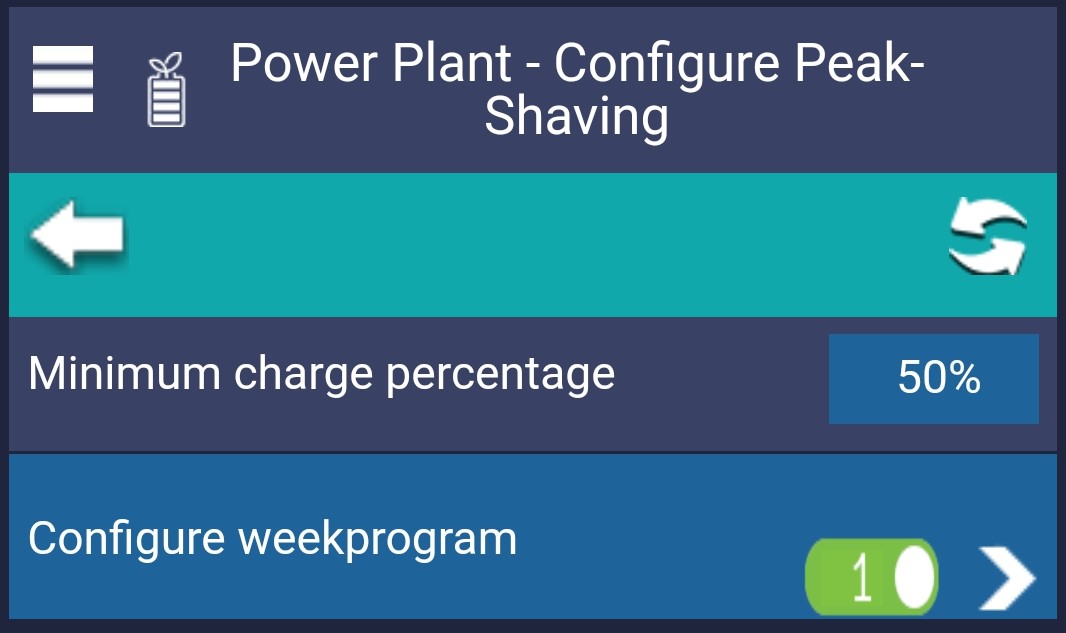
On this page, you can set the minimum charging percentage. This is the limit to which the inverter will charge its battery outside the peak-shaving period so that the battery is charged for the next peak-shaving period.
Under Configure Weekly Schedule, you can activate whether peak-shaving should be active and then specify in which periods peak-shaving should be active.
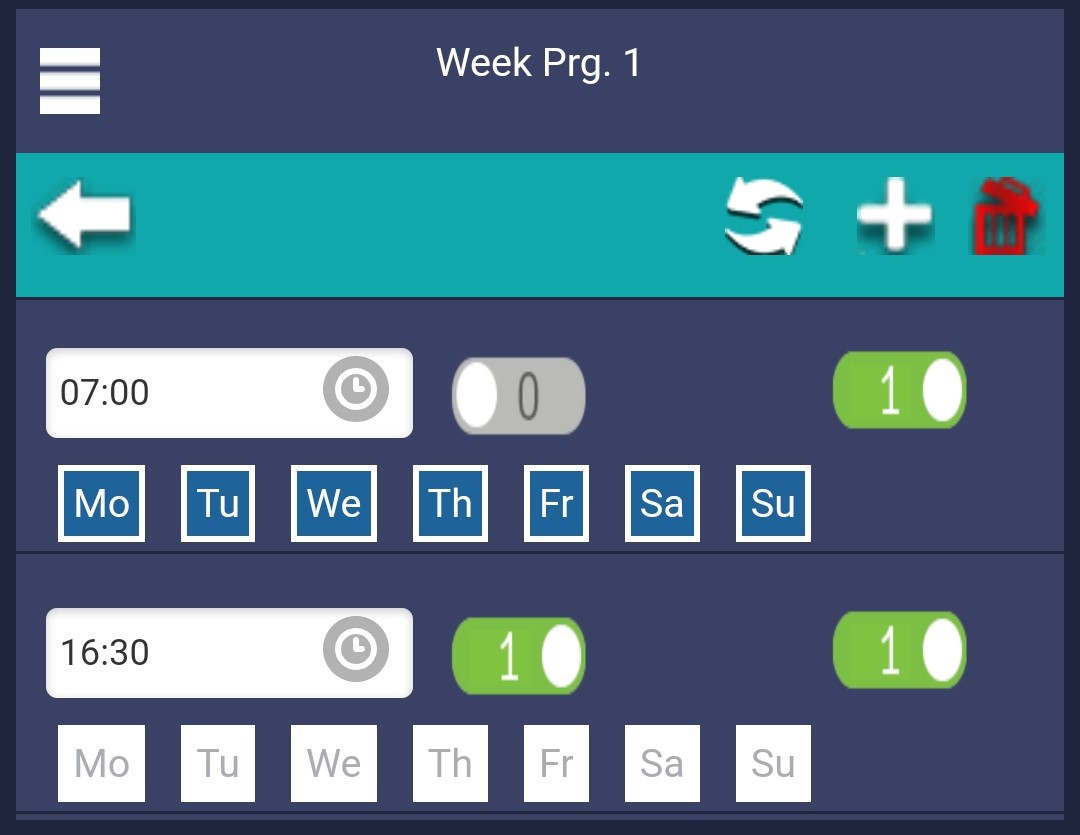
This is our standard weekly schedule functionality. Here, you can configure the time periods during which peak-shaving should be active and when the inverter has the opportunity to recharge its battery.
In the example in the image above, peak-shaving is activated at 7:00 AM every day and deactivated at 4:30 PM. This means that every day of the week between 7:00 AM and 4:30 PM, peak-shaving will cover peak loads that exceed your import limit. From 4:30 PM to 7:00 AM the next day, the inverter will attempt to charge the battery to the minimum charging percentage.
¶ Modes
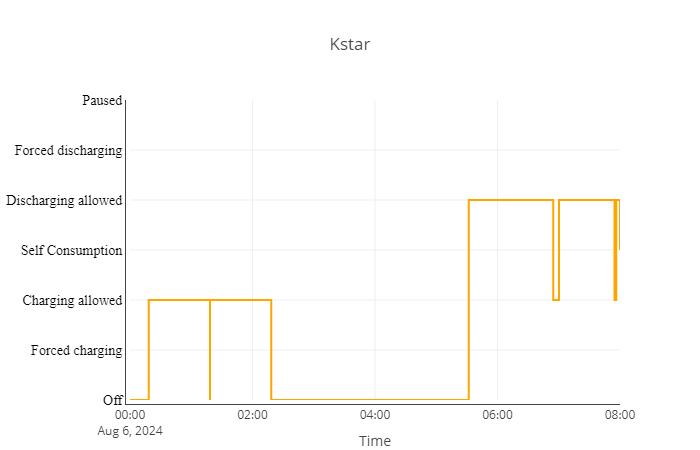
VPP (Virtual Power Plant) has six different modes:
- Pause (The system has no control over the inverter. In this mode, the inverter can be controlled by another service):
- This algorithm cannot put the system into this mode.
- Forced Discharge (Discharges the battery to the grid):
- If the load exceeds the import limit, the system will enter this mode.
- Discharge Allowed (The system allows discharging the battery to balance the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot put the system into this mode.
- Charging Allowed (The system allows charging the battery to balance the main meter to 0):
- This algorithm cannot put the system into this mode.
- Forced Charging (Charges the battery from the grid):
- If peak-shaving is deactivated and the current charging percentage is less than the configured minimum, the system will enter this mode.
- Off (The system functions as a regular grid-connected inverter, where solar production is sent to the grid without charging or discharging the battery):
- This algorithm cannot put the system into this mode.
¶ Graph
¶ Charging power
The graph illustrates the battery's effect over time. The current power going into or out of the battery is displayed in kilowatts (kW). A positive number indicates that the battery is delivering power, while a negative number indicates that the battery is charging.
¶ Charging state
The graph shows the current charge status of the battery in percentage, which can vary from 0% to 100%. The state of charge is measured as a percentage and indicates the amount of energy left in the battery.
¶ Main meter
The graph shows the historical electricity consumption in the house based on electricity meter data. A positive number indicates that the house has an electricity consumption, while a negative number indicates that excess power is sent back to the grid.